https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000004617028
[TOC]
mybatis 中使用 sqlMap 进行 sql 查询时,经常需要动态传递参数,例如我们需要根据用户的姓名来筛选用户时,sql 如下:
~~~
select * from user where name = "ruhua";
~~~
上述 sql 中,我们希望 name 后的参数 "ruhua" 是动态可变的,即不同的时刻根据不同的姓名来查询用户。在 sqlMap 的 xml 文件中使用如下的 sql 可以实现动态传递参数 name:
~~~
select * from user where name = #{name};
~~~
或者
~~~
select * from user where name = '${name}';
~~~
对于上述这种查询情况来说,使用 #{ } 和 ${ } 的结果是相同的,但是在某些情况下,我们只能使用二者其一。
## '#' 与 '$'
### 区别
**动态 SQL** 是 mybatis 的强大特性之一,也是它优于其他 ORM 框架的一个重要原因。mybatis 在对 sql 语句进行预编译之前,会对 sql 进行动态解析,解析为一个 BoundSql 对象,也是在此处对动态 SQL 进行处理的。
在动态 SQL 解析阶段, #{ } 和 ${ } 会有不同的表现:
> **#{ } 解析为一个 JDBC 预编译语句(prepared statement)的参数标记符。**
例如,sqlMap 中如下的 sql 语句
~~~
select * from user where name = #{name};
~~~
解析为:
~~~
select * from user where name = ?;
~~~
一个 #{ } 被解析为一个参数占位符 `?` 。
而,
> **${ } 仅仅为一个纯碎的 string 替换,在动态 SQL 解析阶段将会进行变量替换**
例如,sqlMap 中如下的 sql
~~~
select * from user where name = '${name}';
~~~
当我们传递的参数为 "ruhua" 时,上述 sql 的解析为:
~~~
select * from user where name = "ruhua";
~~~
预编译之前的 SQL 语句已经不包含变量 name 了。
综上所得, ${ } 的变量的替换阶段是在动态 SQL 解析阶段,而 #{ }的变量的替换是在 DBMS 中。
### 用法 tips
> 1、能使用 #{ } 的地方就用 #{ }
首先这是为了性能考虑的,相同的预编译 sql 可以重复利用。
其次,**${ } 在预编译之前已经被变量替换了,这会存在 sql 注入问题**。例如,如下的 sql,
~~~
select * from ${tableName} where name = #{name}
~~~
假如,我们的参数 tableName 为 `user; delete user; --`,那么 SQL 动态解析阶段之后,预编译之前的 sql 将变为
~~~
select * from user; delete user; -- where name = ?;
~~~
`--` 之后的语句将作为注释,不起作用,因此本来的一条查询语句偷偷的包含了一个删除表数据的 SQL!
> 2、表名作为变量时,必须使用 ${ }
这是因为,表名是字符串,使用 sql 占位符替换字符串时会带上单引号 `''`,这会导致 sql 语法错误,例如:
~~~
select * from #{tableName} where name = #{name};
~~~
预编译之后的sql 变为:
~~~
select * from ? where name = ?;
~~~
假设我们传入的参数为 tableName = "user" , name = "ruhua",那么在占位符进行变量替换后,sql 语句变为
~~~
select * from 'user' where name='ruhua';
~~~
上述 sql 语句是存在语法错误的,表名不能加单引号 `''`(注意,反引号 ``是可以的)。
## sql预编译
### 定义
> sql 预编译指的是数据库驱动在发送 sql 语句和参数给 DBMS 之前对 sql 语句进行编译,这样 DBMS 执行 sql 时,就不需要重新编译。
### 为什么需要预编译
JDBC 中使用对象 PreparedStatement 来抽象预编译语句,使用预编译
1. **预编译阶段可以优化 sql 的执行**。
预编译之后的 sql 多数情况下可以直接执行,DBMS 不需要再次编译,越复杂的sql,编译的复杂度将越大,预编译阶段可以合并多次操作为一个操作。
2. **预编译语句对象可以重复利用**。
把一个 sql 预编译后产生的 PreparedStatement 对象缓存下来,下次对于同一个sql,可以直接使用这个缓存的 PreparedState 对象。
mybatis 默认情况下,将对所有的 sql 进行预编译。
### mysql预编译源码解析
mysql 的预编译源码在 `com.mysql.jdbc.ConnectionImpl` 类中,如下:
~~~
public synchronized java.sql.PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql,
int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {
checkClosed();
//
// FIXME: Create warnings if can't create results of the given
// type or concurrency
//
PreparedStatement pStmt = null;
boolean canServerPrepare = true;
// 不同的数据库系统对sql进行语法转换
String nativeSql = getProcessEscapeCodesForPrepStmts() ? nativeSQL(sql): sql;
// 判断是否可以进行服务器端预编译
if (this.useServerPreparedStmts && getEmulateUnsupportedPstmts()) {
canServerPrepare = canHandleAsServerPreparedStatement(nativeSql);
}
// 如果可以进行服务器端预编译
if (this.useServerPreparedStmts && canServerPrepare) {
// 是否缓存了PreparedStatement对象
if (this.getCachePreparedStatements()) {
synchronized (this.serverSideStatementCache) {
// 从缓存中获取缓存的PreparedStatement对象
pStmt = (com.mysql.jdbc.ServerPreparedStatement)this.serverSideStatementCache.remove(sql);
if (pStmt != null) {
// 缓存中存在对象时对原 sqlStatement 进行参数清空等
((com.mysql.jdbc.ServerPreparedStatement)pStmt).setClosed(false);
pStmt.clearParameters();
}
if (pStmt == null) {
try {
// 如果缓存中不存在,则调用服务器端(数据库)进行预编译
pStmt = ServerPreparedStatement.getInstance(getLoadBalanceSafeProxy(), nativeSql,
this.database, resultSetType, resultSetConcurrency);
if (sql.length() < getPreparedStatementCacheSqlLimit()) {
((com.mysql.jdbc.ServerPreparedStatement)pStmt).isCached = true;
}
// 设置返回类型以及并发类型
pStmt.setResultSetType(resultSetType);
pStmt.setResultSetConcurrency(resultSetConcurrency);
} catch (SQLException sqlEx) {
// Punt, if necessary
if (getEmulateUnsupportedPstmts()) {
pStmt = (PreparedStatement) clientPrepareStatement(nativeSql, resultSetType, resultSetConcurrency, false);
if (sql.length() < getPreparedStatementCacheSqlLimit()) {
this.serverSideStatementCheckCache.put(sql, Boolean.FALSE);
}
} else {
throw sqlEx;
}
}
}
}
} else {
// 未启用缓存时,直接调用服务器端进行预编译
try {
pStmt = ServerPreparedStatement.getInstance(getLoadBalanceSafeProxy(), nativeSql,
this.database, resultSetType, resultSetConcurrency);
pStmt.setResultSetType(resultSetType);
pStmt.setResultSetConcurrency(resultSetConcurrency);
} catch (SQLException sqlEx) {
// Punt, if necessary
if (getEmulateUnsupportedPstmts()) {
pStmt = (PreparedStatement) clientPrepareStatement(nativeSql, resultSetType, resultSetConcurrency, false);
} else {
throw sqlEx;
}
}
}
} else {
// 不支持服务器端预编译时调用客户端预编译(不需要数据库 connection )
pStmt = (PreparedStatement) clientPrepareStatement(nativeSql, resultSetType, resultSetConcurrency, false);
}
return pStmt;
}
~~~
流程图如下所示:
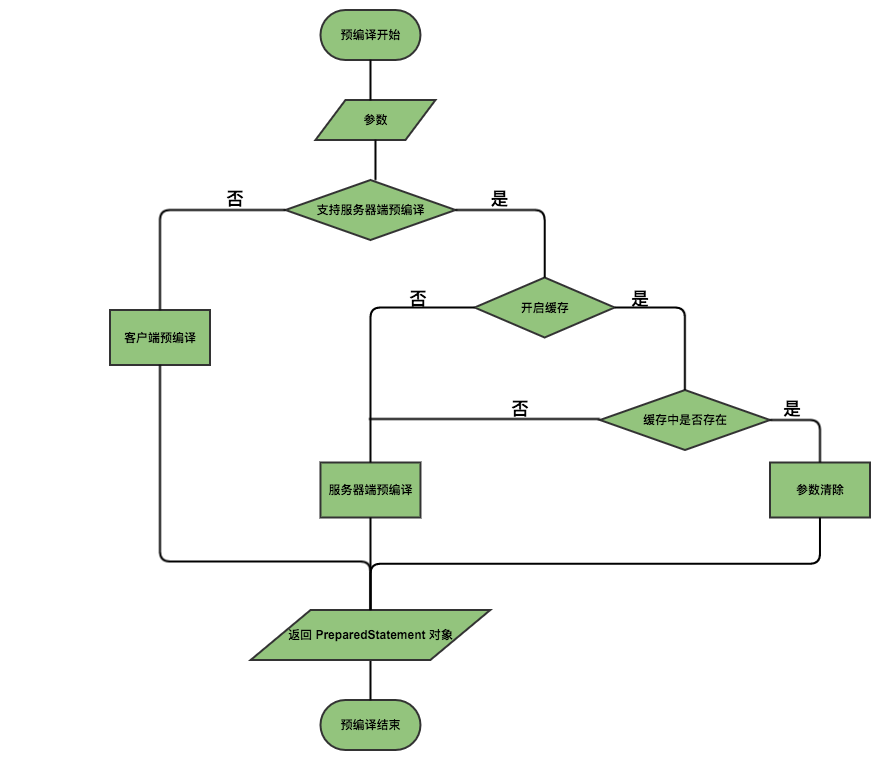
## mybatis之sql动态解析以及预编译源码
### mybatis sql 动态解析
mybatis 在调用 connection 进行 sql 预编译之前,会对sql语句进行动态解析,动态解析主要包含如下的功能:
* 占位符的处理
* 动态sql的处理
* 参数类型校验
mybatis强大的动态SQL功能的具体实现就在此。动态解析涉及的东西太多,以后再讨论。
## 总结
本文主要深入探究了 mybatis 对 #{ } 和 ${ }的不同处理方式,并了解了 sql 预编译。
- 数据库
- CAP定理
- 关系模型
- 关系数据库
- NoSQL
- ODBC
- JDBC
- ODBC、JDBC和四种驱动类型
- mysql
- 安装与配置
- CentOS 7 安装 MySQL
- 优化
- 比较全面的MySQL优化参考
- 1、硬件层相关优化
- 1.1、CPU相关
- 1.2、磁盘I/O相关
- 2、系统层相关优化
- 2.1、文件系统层优化
- 2.2、其他内核参数优化
- 3、MySQL层相关优化
- 3.1、关于版本选择
- 3.2、关于最重要的参数选项调整建议
- 3.3、关于Schema设计规范及SQL使用建议
- 3.4、其他建议
- 后记
- Mysql设计与优化专题
- ER图,数据建模与数据字典
- 数据中设计中的范式与反范式
- 字段类型与合理的选择字段类型
- 表的垂直拆分和水平拆分
- 详解慢查询
- mysql的最佳索引攻略
- 高手详解SQL性能优化十条经验
- 优化SQL查询:如何写出高性能SQL语句
- MySQL索引原理及慢查询优化
- 数据库SQL优化大总结之 百万级数据库优化方案
- 数据库性能优化之SQL语句优化1
- 【重磅干货】看了此文,Oracle SQL优化文章不必再看!
- MySQL 对于千万级的大表要怎么优化?
- MySQL 数据库设计总结
- MYSQL性能优化的最佳20+条经验
- 数据操作
- 数据语句操作类型
- DCL
- 修改Mysql数据库名的5种方法
- DML
- 连接
- 连接2
- DDL
- 数据类型
- 字符集
- 表引擎
- 索引
- MySQL理解索引、添加索引的原则
- mysql建索引的几大原则
- 浅谈mysql的索引设计原则以及常见索引的区别
- 常用工具简介
- QA
- MySQL主机127.0.0.1与localhost区别总结
- 视图(view)
- 触发器
- 自定义函数和存储过程的使用
- 事务(transaction)
- 范式与反范式
- 常用函数
- MySQL 数据类型 详解
- Mysql数据库常用分库和分表方式
- 隔离级别
- 五分钟搞清楚MySQL事务隔离级别
- mysql隔离级别及事务传播
- 事务隔离级别和脏读的快速入门
- 数据库引擎中的隔离级别
- 事务隔离级别
- Innodb中的事务隔离级别和锁的关系
- MySQL 四种事务隔离级的说明
- Innodb锁机制:Next-Key Lock 浅谈
- SQL函数和存储过程的区别
- mongo
- MongoDB设置访问权限、设置用户
- redis
- ORM
- mybatis
- $ vs #
- mybatis深入理解(一)之 # 与 $ 区别以及 sql 预编译
- 电商设计
- B2C电子商务系统研发——概述篇
- B2C电子商务系统研发——商品数据模型设计
- B2C电子商务系统研发——商品模块E-R图建模
- B2C电子商务系统研发——商品SKU分析和设计(一)
- B2C电子商务系统研发——商品SKU分析和设计(二)
- 数据库命名规范--通用
