# 1. 前言
当然,我们所使用的就是之前使用过的`SQLite`数据库。可以简单回顾一下在`java`中是如何操作数据库的:
- 继承自`SQLiteOpenHelper`类,复写对应的方法,可以得到一个`Helper`实例;
- 通过`SQLiteOpenHelper`的实例的`getWritableDatabase()`来得到一个数据库实例;
- 然后就可以通过这个数据库实例进行`CRUD`操作;
简单回顾一下在`Java`中的流程:
```
// 构建一个子类Helper
public class MySQLiteOpenHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
private Context context;
private String name;
private String bookSql = "create table Book (id integer primary key autoincrement, " +
"name text, pages integer)";
private String userSql = "create table User (name text, age integer)";
public MySQLiteOpenHelper(@Nullable Context context,
@Nullable String name,
@Nullable SQLiteDatabase.CursorFactory factory,
int version) {
super(context, name, factory, version);
this.context = context;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
// 创建数据库表
db.execSQL(bookSql);
db.execSQL(userSql);
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
db.execSQL("drop table if exists Book");
db.execSQL("drop table if exists User");
onCreate(db); // 重新执行一下onCreate方法
}
}
// 获取db对象
mySQLiteOpenHelper = new MySQLiteOpenHelper(getApplicationContext(),
"BookDatabase.db", null, 3);
SQLiteDatabase db= mySQLiteOpenHelper.getWritableDatabase();
// CRUD
db.insert("Book", null, values);
```
# 2. Kotlin中的数据库操作
虽然在`Kotlin`中也可以像上面的那种方式一样来进行数据库的操作,但是`Google`推出了一款数据库框架,即:`Room`。下面就使用这个框架进行完成操作。
## 2.1 依赖
首先需要添加依赖:
~~~
// Room
def room_version = "2.2.6"
implementation "androidx.room:room-runtime:$room_version"
// For Kotlin use kapt instead of annotationProcessor (注意这个注释)
kapt "androidx.room:room-compiler:$room_version"
implementation "androidx.room:room-ktx:$room_version"
testImplementation "androidx.room:room-testing:$room_version"
~~~
当然,这里在`kotlin`中使用`kapt`,我们需要导入这个插件:
~~~
plugins {
id 'com.android.application'
id 'kotlin-android'
id 'kotlin-kapt'
}
~~~
注释:如果项目是使用`Kotlin`语言来开发的,在添加`room-compiler`的时候使用`kapt`关键字,`java`语言开发的就使用`annotationProcessor`关键字。
## 2.2 基础概念
要想使用`Room`,必须要了解最基础的三个概念:
* `Entity`:实体类,对应的是数据库的一张表结构。需要使用注解 `@Entity` 标记。默认实体类的类名为表名,字段名为数据库中的字段。
* `Dao`:包含访问一系列访问数据库的方法。需要使用注解 `@Dao` 标记。
* `Database`:数据库持有者,作为与应用持久化相关数据的底层连接的主要接入点。需要使用注解 `@Database` 标记。
使用`@Database`注解需满足以下条件:
* 定义的类必须是一个继承于`RoomDatabase`的抽象类。
* 在注解中需要定义与数据库相关联的实体类列表。
* 包含一个没有参数的抽象方法并且返回一个带有注解的 `@Dao`。
注释:以上基础概念摘自:[Jetpack架构组件 — Room入坑详解](https://blog.csdn.net/singwhatiwanna/article/details/104890202/)
### 2.2 1 @Entity
从前面我们知道,`@Entity`作用在类上,该类对应数据库中的一个数据表。属性对应数据库中的字段,那么类似的我们可以指定主键和注释。同样也是使用注解:
* `@PrimaryKey`注解用来标注表的主键,可以使用`autoGenerate = true `来指定了主键自增长;
* `@ColumnInfo`注解用来标注表对应的列的信息比如表名、默认值等等。
* `@Ignore` 注解顾名思义就是忽略这个字段,使用了这个注解的字段将不会在数据库中生成对应的列信息。
## 2.2.2 @Dao
`Dao`类是一个接口,其中定义了一系列的操作数据库的方法。`Room`也为我们的提供了相关的注解,有`@Insert`、`@Delete`、`@Update` 和 `@Query`。
比如:
```
@Query("select * from user where userId = :id")
fun getUserById(id: Long): User
```
### 2.2.3 @Database
首先需要定义一个类,继承自`RoomDatabase`,并添加注解 `@Database` 来标识。
## 2.3 实战
这里我们需要一个数据库来存储用户记事本的数据,大致包括如下内容:
| 字段 | 说明 |
| --- | --- |
| `title` | 标题 |
| `content` | 数据内容 |
| `firstSubmit` | 首次提交时间 |
| `lastModifiy` | 最后一次修改时间 |
| `type` | 类型,普通记事或者待办 |
| `label` | 标签,支持多个,使用`#`号分割 |
| `category` | 分类,工作/学习/生活/... |
| `groupId` | 组号,默认为1,表示单个记录;如果为多个,表示前端显示为重叠 |
那么首先我们需要使用`@Entity`注解来生成逻辑的表(`MFNote`):
~~~
@Entity
class MFNote {
@PrimaryKey(autoGenerate = true)
var noteId: Int = 0
@ColumnInfo(defaultValue = "无标题")
lateinit var title: String
@ColumnInfo(defaultValue = "")
lateinit var content: String
@ColumnInfo(name = "first_submit")
var submit: String? = null
@ColumnInfo(name = "last_modify")
var modify: String? = null
var type: Int = 0
@ColumnInfo(defaultValue = "默认")
lateinit var label: String
@ColumnInfo(defaultValue = "默认")
lateinit var category: String
@ColumnInfo(name = "group_id")
var groupId: Int = 1
}
~~~
然后构建一个访问`MFNote`表的`DAO`接口(`MFDao`):
~~~
@Dao
interface MFDao {
@Insert(onConflict = OnConflictStrategy.REPLACE)
fun insert(mfNote: MFNote?)
@Delete
fun delete(mfNote: MFNote): Int
@Query("select * from MFNote")
fun getAllNotes(): List<MFNote>
@Query("select * from MFNote where type = :type")
fun getNotesByType(type: Int): MFNote
@Update
fun updateNoteByNote(mfNote: MFNote)
}
~~~
参数`onConflict`,表示的是当插入的数据已经存在时候的处理逻辑,有三种操作逻辑:`REPLACE`、`ABORT`和`IGNORE`。如果不指定则默认为`ABORT`终止插入数据。这里我们将其指定为`REPLACE`替换原有数据。
最后需要构建`Room`使用的入口`RoomDatabase`。
~~~
@Database(entities = [MFNote::class], version = 1)
abstract class MFNoteDataBase : RoomDatabase() {
abstract fun mfDao(): MFDao
companion object {
@Volatile
private var mInstance: MFNoteDataBase? = null
private const val DATABASE_NAME = "MFNote.db"
@JvmStatic
fun getInstance(context: Context): MFNoteDataBase? {
if (mInstance == null) {
synchronized(MFNoteDataBase::class.java) {
if (mInstance == null) {
mInstance = createInstance(context)
}
}
}
return mInstance
}
private fun createInstance(context: Context): MFNoteDataBase {
mInstance = Room.databaseBuilder(
context.applicationContext,
MFNoteDataBase::class.java,
DATABASE_NAME
).build()
return mInstance as MFNoteDataBase
}
}
}
~~~
在这里我们只需要对一个数据库表进行操作,所以就定义了一个抽象接口。如果需要定义多个,比如下面的写法:
~~~
@Database(entities = [User::class, Course::class, Teacher::class, UserJoinCourse::class, IDCard::class], version = 1)
abstract class AppDataBase : RoomDatabase() {
abstract fun userDao(): UserDao
abstract fun teacherDao(): TeacherDao
abstract fun courseDao(): CourseDao
abstract fun userJoinCourseDao(): UserJoinCourseDao
abstract fun idCardDao(): IDCardDao
}
~~~
* `@Database` 表示继承自`RoomDatabase`的抽象类,`entities`指定表的实现类列表,`version`指定了`DB`版本
* 必须提供获取`DAO`接口的抽象方法,比如上面定义的`movieDao()`,`Room`将通过这个方法实例化`DAO`接口
接下来就是调用了:
~~~
class TestActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_test)
// 调用Room数据库
val mfDao = MFNoteDataBase.getInstance(this)?.mfDao()
mfDao?.insert(MFNote())
mfDao?.getAllNotes()?.forEach {
Log.e("TAG", "onCreate: ${it.title}, ${it.category}" )
}
}
}
~~~
结果:
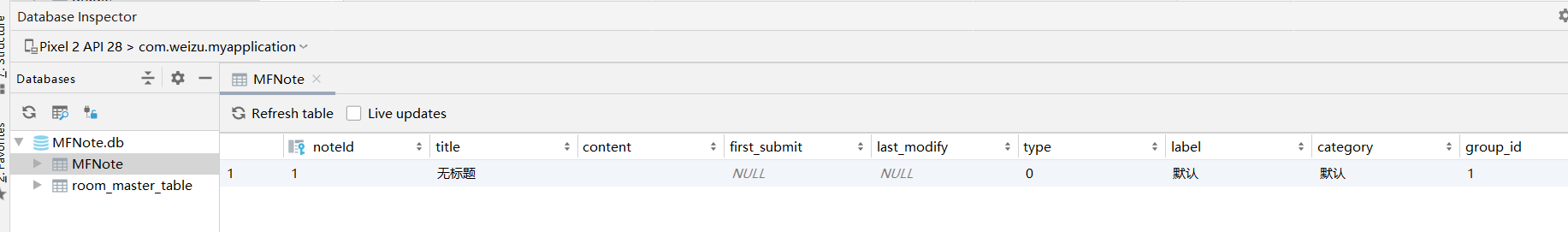
最终我在`Dao`层添加了如下方法:
~~~
@Dao
interface MFDao {
@Insert(onConflict = OnConflictStrategy.REPLACE)
fun insert(mfNote: MFNote?)
@Delete
fun delete(mfNote: MFNote): Int
@Query("select * from MFNote")
fun getAllNotes(): List<MFNote>
@Query("select * from MFNote where noteId = :id")
fun getNoteByNoteId(id: Int): MFNote
@Query("select * from MFNote where type = :type")
fun getNotesByType(type: Int): List<MFNote>
@Query("select * from MFNote where label like '%' || :label || '%'")
fun getNotesByLabel(label: String): List<MFNote>
@Query("select * from MFNote where category like '%' || :category || '%'")
fun getNotesByCategory(category: String): List<MFNote>
@Query("select * from MFNote where group_id = :groupId")
fun getNotesByGroupId(groupId: Int): List<MFNote>
@Query("select * from MFNote where first_submit >= :beginTime and first_submit <= :endTime")
fun getNotesBySubmitTime(beginTime: String, endTime: String): List<MFNote>
@Query("select * from MFNote where first_submit >= :beginTime")
fun getNotesByStartSubmitTime(beginTime: String): List<MFNote>
@Query("select * from MFNote where first_submit <= :endTime")
fun getNotesByEndSubmitTime(endTime: String): List<MFNote>
@Query("select * from MFNote where last_modify >= :beginTime and last_modify <= :endTime")
fun getNotesByModifyTime(beginTime: String, endTime: String): List<MFNote>
@Query("select * from MFNote where last_modify >= :beginTime")
fun getNotesByStartModifyTime(beginTime: String): List<MFNote>
@Query("select * from MFNote where last_modify <= :endTime")
fun getNotesByEndModifyTime(endTime: String): List<MFNote>
@Query("select * from MFNote where (title like '%' || :words || '%') or (content like '%' || :words || '%') or (first_submit like '%' || :words || '%') or (last_modify like '%' || :words || '%') or (label like '%' || :words || '%') or (category like '%' || :words || '%')")
fun getNodesByKeyWords(words: String): List<MFNote>
@Update
fun updateNoteByNote(mfNote: MFNote)
}
~~~
测试代码:
~~~
class TestActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_test)
// 调用Room数据库
val mfDao = MFNoteDataBase.getInstance(this)?.mfDao()
val mfNote = MFNote()
mfNote.title = "测试"
mfNote.content = "第一条测试"
mfDao?.insert(mfNote)
mfDao?.getAllNotes()?.forEach {
Log.e("TAG", "onCreate: ${it.title}, ${it.category}" )
}
val notesByType = mfDao?.getNotesByType(0)
notesByType?.forEach {
Log.e("TAG", "onCreate: ${it.title}, ${it.category}" )
}
val entity = mfDao?.getNoteByNoteId(2)
Log.e("TAG", "onCreate: ${entity?.title}, ${entity?.firstSubmit}" )
entity?.title = "厉害"
mfDao?.updateNoteByNote(entity!!)
}
}
~~~
以上代码均测试通过。
