### 字符数组
~~~
char str1[10] = {'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'}; //后面的元素是 0 0 0 0 0
printf("%s\n", str1); //%s会接受字符串结束标志'\0'之前的所有字符,在ascii码中就是数字0
~~~
```
hello
```
~~~
char str1[10] = {'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'};
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(str1) / sizeof(char); ++i) {
printf("%c", str1[i]);
}
~~~
可以看到打印出的是ascii码中的'\0'就是空字符.

~~~
char str1[10] = {'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'};
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(str1) / sizeof(char); ++i) {
printf("%d\n", str1[i]);
}
~~~
可以看到打印的都是ascii码
```
104
101
108
108
111
0
0
0
0
0
```
### 字符串
~~~
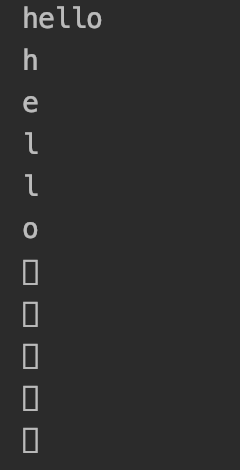
char str2[10] = "hello";
printf("%s\n", str2);
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(str2) / sizeof(char); ++i) {
printf("%c\n", str2[i]);
}
~~~
### 字符串不指定长度
~~~
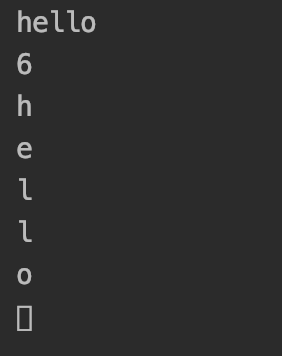
char str2[] = "hello";
printf("%s\n", str2);
printf("%d\n", sizeof(str2)); //6个长度
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(str2) / sizeof(char); ++i) {
printf("%c\n", str2[i]);
}
~~~
可以看到程序会自动的帮我们加上'\0'
~~~
char str3[] = {'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'};
printf("%d\n", sizeof(str3)); //5个长度
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(str3) / sizeof(char); ++i) {
printf("%c\n", str3[i]);
}
~~~
```
5
h
e
l
l
o
```
### 手动加上\0
~~~
char str3[] = "he\0llo";
printf("%d\n", sizeof(str3));
printf("%s\n", str3);
~~~
遇到\0就结束了
```
7
he
```
### 字符数组用%s输出
~~~
char str3[] = {'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'};
printf("%s\n", str3);
printf("%d", sizeof(str3));
~~~
老师演示的是后面会出现乱码,因为用%s输出,必须要找到\0才算结束. 但是这里并没有. 可能是因为标准变了. **千万不要这么来使用**.
```
hello
5
```
### scanf 的问题
**scanf()函数接收输入数据时,遇以下情况结束一个数据的输入**
① 遇空格、“回车”、“跳格”键。
② 遇宽度结束。
③ 遇非法输入
~~~
char str[100];
scanf("%s",str);
printf("%s",str);
~~~
```
hello world
hello //只输出了hello
```
这样才可以
~~~
char str[100];
scanf("%[^\n]",str);
printf("%s",str);
~~~
```
hello world
hello world
```
### 字符串追加
~~~
char str1[] = "hello";
char str2[] = "world";
char str3[100];
int index = 0;
while (str1[index] != '\0') {
str3[index] = str1[index];
index++;
}
while (str2[index - 5] != '\0') {
str3[index] = str2[index - 5];
index++;
}
~~~
### 字符串和字符数组在内存中不同的存储方式
