# 实现 DeepDream
受过训练的 CNN 的另一个用途是利用一些中间节点检测标签特征(例如,猫的耳朵或鸟的羽毛)的事实。利用这一事实,我们可以找到转换任何图像的方法,以反映我们选择的任何节点的节点特征。对于这个秘籍,我们将在 TensorFlow 的网站上浏览 DeepDream 教程,但我们将更详细地介绍基本部分。希望我们可以让读者准备好使用 DeepDream 算法来探索 CNN 及其中创建的特征。
## 做好准备
TensorFlow 的官方教程展示了如何通过脚本实现 DeepDream(请参阅下一节中的第一个要点)。这个方法的目的是通过他们提供的脚本并解释每一行。虽然教程很棒,但有些部分可以跳过,有些部分可以使用更多解释。我们希望提供更详细的逐行说明。我们还将在必要时使代码符合 Python 3 标准。
## 操作步骤
执行以下步骤:
1. 为了开始使用 DeepDream,我们需要下载在 CIFAR-1000 上接受过 CNN 训练的 GoogleNet:
```py
me@computer:~$ wget https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/models/inception5h.zip
me@computer:~$ unzip inception5h.zip
```
1. 我们首先加载必要的库并开始图会话:
```py
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import PIL.Image
import tensorflow as tf
from io import BytesIO
graph = tf.Graph()
sess = tf.InteractiveSession(graph=graph)
```
1. 我们现在声明解压缩模型参数的位置(从步骤 1 开始)并将参数加载到 TensorFlow 图中:
```py
# Model location
model_fn = 'tensorflow_inception_graph.pb'
# Load graph parameters
with tf.gfile.FastGFile(model_fn, 'rb') as f:
graph_def = tf.GraphDef()
graph_def.ParseFromString(f.read())
```
1. 我们为输入创建一个占位符,保存 imagenet 平均值 117.0,然后使用正则化占位符导入图定义:
```py
# Create placeholder for input
t_input = tf.placeholder(np.float32, name='input')
# Imagenet average bias to subtract off images
imagenet_mean = 117.0
t_preprocessed = tf.expand_dims(t_input-imagenet_mean, 0)
tf.import_graph_def(graph_def, {'input':t_preprocessed})
```
1. 接下来,我们将导入卷积层,以便在以后可视化并使用它们进行 DeepDream 处理:
```py
# Create a list of layers that we can refer to later
layers = [op.name for op in graph.get_operations() if op.type=='Conv2D' and 'import/' in op.name]
# Count how many outputs for each layer
feature_nums = [int(graph.get_tensor_by_name(name+':0').get_shape()[-1]) for name in layers]
```
1. 现在我们将选择一个可视化的层。我们也可以通过名字选择其他人。我们选择查看特征号`139`。图像以随机噪声开始:
```py
layer = 'mixed4d_3x3_bottleneck_pre_relu'
channel = 139
img_noise = np.random.uniform(size=(224,224,3)) + 100.0
```
1. 我们声明了一个绘制图像数组的函数:
```py
def showarray(a, fmt='jpeg'):
# First make sure everything is between 0 and 255
a = np.uint8(np.clip(a, 0, 1)*255)
# Pick an in-memory format for image display
f = BytesIO()
# Create the in memory image
PIL.Image.fromarray(a).save(f, fmt)
# Show image
plt.imshow(a)
```
1. 我们将通过创建一个从图中按名称检索层的函数来缩短一些重复代码:
```py
def T(layer): #Helper for getting layer output tensor return graph.get_tensor_by_name("import/%s:0"%layer)
```
1. 我们将创建的下一个函数是一个包装函数,用于根据我们指定的参数创建占位符:
```py
# The following function returns a function wrapper that will create the placeholder
# inputs of a specified dtype
def tffunc(*argtypes):
'''Helper that transforms TF-graph generating function into a regular one.
See "resize" function below.
'''
placeholders = list(map(tf.placeholder, argtypes))
def wrap(f):
out = f(*placeholders)
def wrapper(*args, **kw):
return out.eval(dict(zip(placeholders, args)), session=kw.get('session'))
return wrapper
return wrap
```
1. 我们还需要一个将图像大小调整为大小规格的函数。我们使用 TensorFlow 的内置图像线性插值函数:`tf.image.resize.bilinear()`
```py
# Helper function that uses TF to resize an image
def resize(img, size):
img = tf.expand_dims(img, 0)
# Change 'img' size by linear interpolation
return tf.image.resize_bilinear(img, size)[0,:,:,:]
```
1. 现在我们需要一种方法来更新源图像,使其更像我们使用的特征。我们通过指定如何计算图像上的梯度来完成此操作。我们定义了一个函数,用于计算图像上子区域(图块)的梯度,以加快计算速度。为了防止平铺输出,我们将在`x`和`y`方向上随机移动或滚动图像,这将平滑平铺效果:
```py
def calc_grad_tiled(img, t_grad, tile_size=512):
'''Compute the value of tensor t_grad over the image in a tiled way.
Random shifts are applied to the image to blur tile boundaries over
multiple iterations.'''
# Pick a subregion square size
sz = tile_size
# Get the image height and width
h, w = img.shape[:2]
# Get a random shift amount in the x and y direction
sx, sy = np.random.randint(sz, size=2)
# Randomly shift the image (roll image) in the x and y directions
img_shift = np.roll(np.roll(img, sx, 1), sy, 0)
# Initialize the while image gradient as zeros
grad = np.zeros_like(img)
# Now we loop through all the sub-tiles in the image
for y in range(0, max(h-sz//2, sz),sz):
for x in range(0, max(w-sz//2, sz),sz):
# Select the sub image tile
sub = img_shift[y:y+sz,x:x+sz]
# Calculate the gradient for the tile
g = sess.run(t_grad, {t_input:sub})
# Apply the gradient of the tile to the whole image gradient
grad[y:y+sz,x:x+sz] = g
# Return the gradient, undoing the roll operation
return np.roll(np.roll(grad, -sx, 1), -sy, 0)
```
1. 现在我们可以声明 DeepDream 函数。我们算法的目标是我们选择的特征的平均值。损耗在梯度上运行,这取决于输入图像和所选特征之间的距离。策略是将图像分成高频和低频,并计算低频部分的梯度。将得到的高频图像再次分开并重复该过程。原始图像和低频图像的集合称为`octaves`。对于每次传递,我们计算梯度并将它们应用于图像:
```py
def render_deepdream(t_obj, img0=img_noise,
iter_n=10, step=1.5, octave_n=4, octave_scale=1.4):
# defining the optimization objective, the objective is the mean of the feature
t_score = tf.reduce_mean(t_obj)
# Our gradients will be defined as changing the t_input to get closer to the values of t_score. Here, t_score is the mean of the feature we select.
# t_input will be the image octave (starting with the last)
t_grad = tf.gradients(t_score, t_input)[0] # behold the power of automatic differentiation!
# Store the image
img = img0
# Initialize the image octave list
octaves = []
# Since we stored the image, we need to only calculate n-1 octaves
for i in range(octave_n-1):
# Extract the image shape
hw = img.shape[:2]
# Resize the image, scale by the octave_scale (resize by linear interpolation)
lo = resize(img, np.int32(np.float32(hw)/octave_scale))
# Residual is hi. Where residual = image - (Resize lo to be hw-shape)
hi = img-resize(lo, hw)
# Save the lo image for re-iterating
img = lo
# Save the extracted hi-image
octaves.append(hi)
# generate details octave by octave
for octave in range(octave_n):
if octave>0:
# Start with the last octave
hi = octaves[-octave]
#
img = resize(img, hi.shape[:2])+hi
for i in range(iter_n):
# Calculate gradient of the image.
g = calc_grad_tiled(img, t_grad)
# Ideally, we would just add the gradient, g, but
# we want do a forward step size of it ('step'),
# and divide it by the avg. norm of the gradient, so
# we are adding a gradient of a certain size each step.
# Also, to make sure we aren't dividing by zero, we add 1e-7\.
img += g*(step / (np.abs(g).mean()+1e-7))
print('.',end = ' ')
showarray(img/255.0)
```
1. 通过我们所做的所有特征设置,我们现在可以运行 DeepDream 算法:
```py
# Run Deep Dream
if __name__=="__main__":
# Create resize function that has a wrapper that creates specified placeholder types
resize = tffunc(np.float32, np.int32)(resize)
# Open image
img0 = PIL.Image.open('book_cover.jpg')
img0 = np.float32(img0)
# Show Original Image
showarray(img0/255.0)
# Create deep dream
render_deepdream(T(layer)[:,:,:,139], img0, iter_n=15)
sess.close()
```
输出如下:
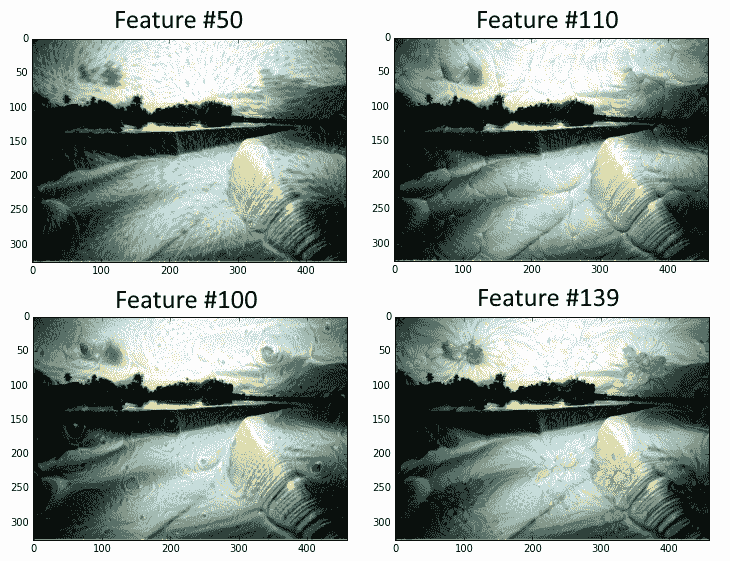
图 7:本书的封面,贯穿 DeepDream 算法,其特征层编号为 50,110,100 和 139
## 更多
我们敦促读者使用官方 DeepDream 教程作为进一步信息的来源,并访问 DeepDream 上的原始 Google 研究博客文章(请参阅下面的第二个要点参见另请参阅部分)。
## 另见
* DeepDream 上的 TensorFlow 教程: [https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/tree/master/tensorflow/examples/tutorials/deepdream](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/tree/master/tensorflow/examples/tutorials/deepdream)
* 关于 DeepDream 的最初 Google 研究博客文章: [https://research.googleblog.com/2015/06/inceptionism-going-deeper-into-neural.html](https://research.googleblog.com/2015/06/inceptionism-going-deeper-into-neural.html)
- TensorFlow 入门
- 介绍
- TensorFlow 如何工作
- 声明变量和张量
- 使用占位符和变量
- 使用矩阵
- 声明操作符
- 实现激活函数
- 使用数据源
- 其他资源
- TensorFlow 的方式
- 介绍
- 计算图中的操作
- 对嵌套操作分层
- 使用多个层
- 实现损失函数
- 实现反向传播
- 使用批量和随机训练
- 把所有东西结合在一起
- 评估模型
- 线性回归
- 介绍
- 使用矩阵逆方法
- 实现分解方法
- 学习 TensorFlow 线性回归方法
- 理解线性回归中的损失函数
- 实现 deming 回归
- 实现套索和岭回归
- 实现弹性网络回归
- 实现逻辑回归
- 支持向量机
- 介绍
- 使用线性 SVM
- 简化为线性回归
- 在 TensorFlow 中使用内核
- 实现非线性 SVM
- 实现多类 SVM
- 最近邻方法
- 介绍
- 使用最近邻
- 使用基于文本的距离
- 使用混合距离函数的计算
- 使用地址匹配的示例
- 使用最近邻进行图像识别
- 神经网络
- 介绍
- 实现操作门
- 使用门和激活函数
- 实现单层神经网络
- 实现不同的层
- 使用多层神经网络
- 改进线性模型的预测
- 学习玩井字棋
- 自然语言处理
- 介绍
- 使用词袋嵌入
- 实现 TF-IDF
- 使用 Skip-Gram 嵌入
- 使用 CBOW 嵌入
- 使用 word2vec 进行预测
- 使用 doc2vec 进行情绪分析
- 卷积神经网络
- 介绍
- 实现简单的 CNN
- 实现先进的 CNN
- 重新训练现有的 CNN 模型
- 应用 StyleNet 和 NeuralStyle 项目
- 实现 DeepDream
- 循环神经网络
- 介绍
- 为垃圾邮件预测实现 RNN
- 实现 LSTM 模型
- 堆叠多个 LSTM 层
- 创建序列到序列模型
- 训练 Siamese RNN 相似性度量
- 将 TensorFlow 投入生产
- 介绍
- 实现单元测试
- 使用多个执行程序
- 并行化 TensorFlow
- 将 TensorFlow 投入生产
- 生产环境 TensorFlow 的一个例子
- 使用 TensorFlow 服务
- 更多 TensorFlow
- 介绍
- 可视化 TensorBoard 中的图
- 使用遗传算法
- 使用 k 均值聚类
- 求解常微分方程组
- 使用随机森林
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras
