# Serial Differencing Aggregation(串行差异聚合)
原文链接 : [https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/5.4/search-aggregations-pipeline-serialdiff-aggregation.html](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/5.4/search-aggregations-pipeline-serialdiff-aggregation.html)
译文链接 : [http://www.apache.wiki/pages/createpage-entervariables.action?templateId=4816898&spaceKey=Elasticsearch&title=&newSpaceKey=Elasticsearch&fromPageId=10029316](http://www.apache.wiki/pages/createpage-entervariables.action?templateId=4816898&spaceKey=Elasticsearch&title=&newSpaceKey=Elasticsearch&fromPageId=10029316)
贡献者 : [程威](/display/~chengwei),[ApacheCN](/display/~apachecn),[Apache中文网](/display/~apachechina)
Warning
这个功能是实验性的,可能会在将来的版本完全更改或者移除。Elastic将采取最大的努力来解决任何问题,但实验性的功能不受SLA官方功能的支持。
串行差分是将在一个时间序列中的值减去其本身滞后一段时间或周期的值。例如,数据点 f(x) = f(xt) - f(xt-n),其中n是所使用的周期。
周期1相当于没有时间归一化的导数:它表是从一个点到下一个点的变化。单个周期对于消除不变的线性趋势很有用。
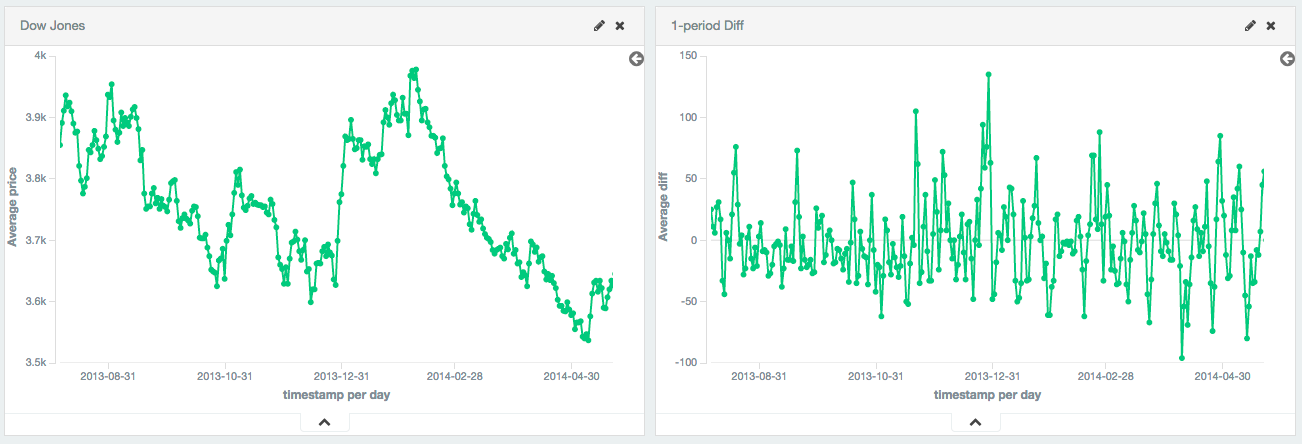
单个周期也可用于将数据转换为固定的序列。在这个例子中,道琼斯指数绘制了超过250天左右。原始数据不是静止的,这会使得很难使用这些数据。
通过计算第一个差值,我们去除趋势数据(例如删除常数,线性趋势)。我们可以看到数据成为一个固定的序列(例如,第一个差异是随机分布在零值附近,似乎没有任何模式/行为)。这个转换揭示了数据集是随机游走的;该值是先前的值加减随机随机。这种洞察允许选择进一步的分析工具。
图15\. 道琼斯数据绘画和通过第一个差值来稳定数据。
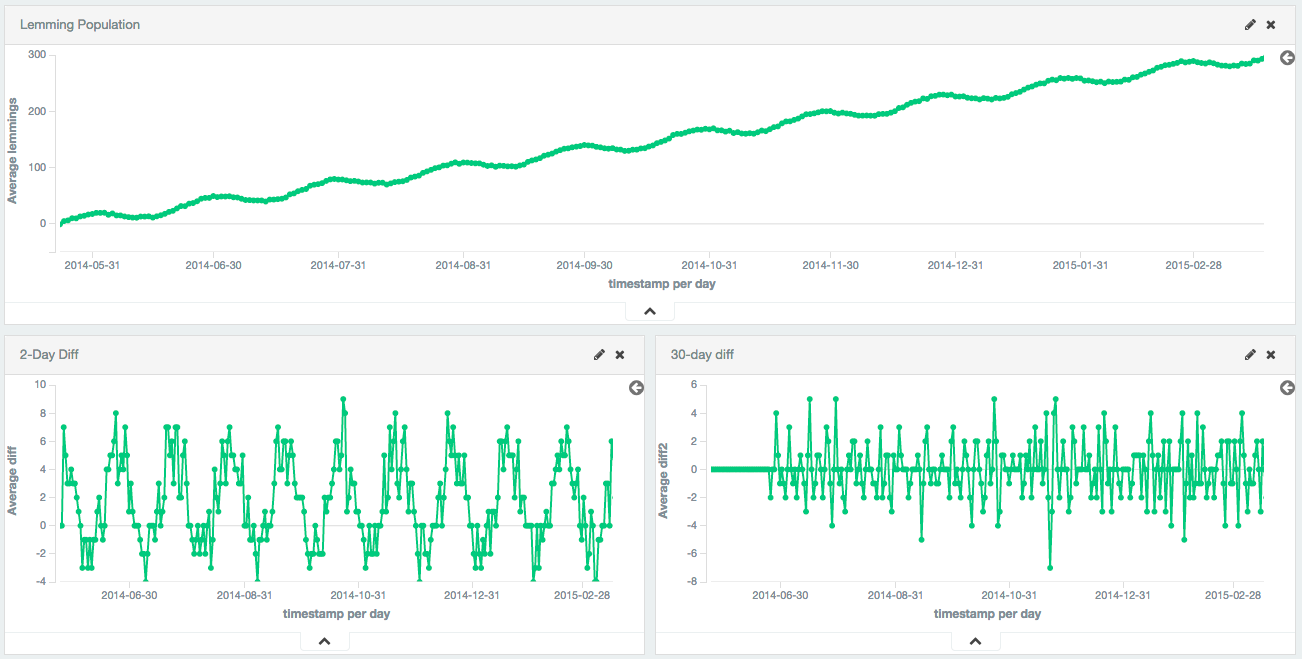
可以使用更大的时间段来消除季节性/循环性。在这个例子中,以正弦波+恒定线性趋势+随机噪声综合生成了一个引理群。正弦波有30天的时间。
第一个差异消除了恒定的趋势,只剩下一个正弦波。然后将第30个差值应用于第一个差异以消除循环行为,留下适合于其他分析的固定序列。
图16.绘制了第一和第30个差异的静止数据
## Syntax(句法)
**serial_diff** 聚合看起来像这样:
```
{
"serial_diff": {
"buckets_path": "the_sum",
"lag": "7"
}
}
```
Table 13\. serial_diff 参数
| 参数名称 | 描述 | 是否必填 | 默认值 |
| --- | --- | --- | --- |
| buckets_path | 感兴趣的度量的路径(更多细节可以看[buckets_path](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/5.4/search-aggregations-pipeline.html#buckets-path-syntax) 语法) | 必填 | |
| lag | 从当前的值减去历史 **bucket**。比如,lag=7表示每次从当前的 **bucket** 的值减去其前面第7个 **bucket** 的值。必须是非零正整数。 | 可选 | 1 |
| gap_policy | 确定遇到数据间隙时的策略 | 可选 | insert_zero |
| format | 格式化聚合输出的值 | 可选 | null |
**serial_diff** 聚合必须嵌入到 **histogram** 或者 **date_histogram** 聚合中:
```
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/_search?pretty' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"my_date_histo": { 1
"date_histogram": {
"field": "timestamp",
"interval": "day"
},
"aggs": {
"the_sum": {
"sum": {
"field": "lemmings" 2
}
},
"thirtieth_difference": {
"serial_diff": { 3
"buckets_path": "the_sum",
"lag" : 30
}
}
}
}
}
}
'
```
| 1 | 一个命名为“**date_histogram**” 的 **date_histogram** , 由 timestamp 字段和 一天间隔组成。 |
| 2 | **sum** 度量是用来计算字段的和。可以填很多值(sum, min, max, etc) |
| 3 | 最后,我们指定一个以 **the_sum** 作为输入的 **serial_diff** 聚合。 |
串行差分通过在字段上指定 **histogram **或者 **date_histogram**。你可以选择选择性的添加常规的度量,例如sum。最后 **serial_diff **被嵌入到 **histogram中**。然后 **buckets_path **参数用于指向histogram中的一个同级的度量。(有关buckets_path的语法,请参见[buckets_path](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/5.4/search-aggregations-pipeline.html#buckets-path-syntax) 这节)。
- Getting Started(入门指南)
- Basic Concepts(基础概念)
- Installation(安装)
- Exploring Your Cluster(探索集群)
- Cluster Health(集群健康)
- List All Indices(列出所有索引)
- Create an Index(创建索引)
- Index and Query a Document(索引和查询文档)
- Delete an Index(删除索引)
- Modifying Your Data(修改数据)
- Updating Documents(更新文档)
- Deleting Documents(删除文档)
- Batch Processing(批处理)
- Exploring Your Data(探索数据)
- The Search API(搜索 API)
- Introducing the Query Language(介绍查询语言)
- Executing Searches(执行查询)
- Executing Filters(执行过滤)
- Executing Aggregations(执行聚合)
- Conclusion(总结)
- Setup Elasticsearch(设置)
- Installing Elasticsearch(安装)
- zip 或 tar.gz 安装
- Debian软件包安装Elasticsearch
- 用RPM安装Elasticsearch
- Windows 环境下安装ES
- Docker 方式安装
- 配置Elasticsearch
- 重要Elasticsearch配置
- 安全配置
- 启动前检查
- 堆大小检查
- 文件描述符检查
- 内存锁定检查
- 最大线程数检查
- 最大虚拟内存检查
- 最大map数检查
- JVM Client模式检查
- 串行收集使用检查
- 系统调用过滤检查
- OnError与OnOutOfMemoryError检查
- G1GC检查
- 重要的系统配置
- 系统设置
- 在jvm.options中设置JVM堆大小
- 禁用swapping
- 文件描述符
- 虚拟内存
- 线程数
- 升级Elasticsearch
- Elasticsearch停机
- 重大改变
- 在5.3 重大改变
- 在5.2 重大改变
- Shadow Replicas已被弃用
- 在5.1 重大改变
- 在5.0 重大改变
- 搜索和查询DSL改变
- 映射改变
- 过滤器改变
- Suggester变化
- 索引API改变
- 文档API改变
- 设置的改变
- 分配改变
- HTTP改变
- REST API改变
- CAT API改变
- Java API改变
- Packaging
- Plugin改变
- 文件系统相关改变
- 磁盘上数据的路径
- 聚合改变
- 脚本相关改变
- API 规范
- Multiple Indices(多个索引)
- Date math support in index names(索引名称对 Date 和 Math 的支持)
- 常见选项
- URL-based access control(基于 URL 的访问控制)
- Document APIS
- Index API
- Get API
- Update API
- 通过查询 API 更新
- 多个 GET API
- Bulk API
- Reading and Writing documents(读写文档)
- Delete API
- Delete By Query API
- Reindex API
- Term Vectors
- Multi termvectors API
- ?refresh
- Search APIs
- Search
- URI Search
- Request Body Search
- Query
- From / Size
- Sort
- Source filtering
- Fields
- Script Fields
- Doc value Fields
- Post filter
- Highlighting
- Rescoring
- Search Type
- Scroll
- Preference
- Explain
- Version
- Index Boost
- min_score
- Named Queries
- Inner hits
- Search After
- Field Collapsing 字段折叠
- Search 模板
- Multi Search 模板
- Search Shards API
- Suggesters
- Completion Suggester
- Context Suggester
- Phrase Suggester
- Term suggester
- Multi Search API
- Count API
- Validate API
- Explain API
- Profile API
- Profiling Queries
- Profiling Aggregations
- Profiling Considerations
- Aggregations
- Metric Aggregations
- 值计数聚合(Value Count Aggregation)
- 地理边界聚合
- 地理重心聚合
- 基数聚合
- 平均值聚合
- 扩展统计聚合
- 最大值聚合
- 最小值聚合
- Bucket Aggregations
- Children Aggregation
- Date Histogram Aggregation
- Date Range Aggregation
- Diversified Sampler Aggregation
- Filter Aggregation(过滤器聚合)
- Filters Aggregation
- Geo Distance Aggregation(地理距离聚合)
- GeoHash grid Aggregation(GeoHash网格聚合)
- Global Aggregation(全局聚合)
- Histogram Aggregation
- IP Range Aggregation(IP范围聚合)
- Missing Aggregation
- Nested Aggregation(嵌套聚合)
- Range Aggregation(范围聚合)
- Reverse nested Aggregation
- Sampler Aggregation
- Significant Terms Aggregation
- 邻接矩阵聚合
- Pipeline Aggregations
- Avg Bucket Aggregation
- Derivative Aggregation(导数聚合)
- Max Bucket Aggregation
- Min Bucket Aggregation
- Sum Bucket Aggregation
- Stats Bucket Aggregation
- Extended Stats Bucket Aggregation(扩展信息桶聚合)
- Percentiles Bucket Aggregation(百分数桶聚合)
- Cumulative Sum Aggregation(累积汇总聚合)
- Bucket Script Aggregation(桶脚本聚合)
- Bucket Selector Aggregation(桶选择器聚合)
- Serial Differencing Aggregation(串行差异聚合)
- Matrix Aggregations
- Matrix Stats
- Matrix Stats(矩阵统计)
- Caching heavy aggregations(缓存频繁聚合)
- Returning only aggregation results(仅返回需要聚合的结果)
- Aggregation Metadata(聚合元数据)
- Returning the type of the aggregation(返回聚合的类型)
- 索引 API
- Create Index /创建索引
- Delete Index /删除索引
- Get Index /获取索引
- Indices Exists /索引存在
- Open / Close Index API /启动关闭索引
- Shrink Index /缩小索引
- Rollover Index/滚动索引
- Put Mapping /提交映射
- Get Mapping /获取映射
- Get Field Mapping /获取字段映射
- 卷影副本索引
- 依赖卷影副本的节点级设置
- 索引统计信息
- 索引段
- 索引恢复
- 索引分片存储
- 清理缓存
- 刷新
- 同步刷新
- 重新加载
- 强制合并
- cat APIs
- cat aliases
- cat allocation
- cat count
- cat fielddata
- cat health
- cat indices
- cat master
- cat nodeattrs
- cat nodes
- cat pending tasks
- cat plugins
- cat recovery
- cat repositories
- cat thread pool
- cat shards
- cat segments
- cat snapshots
- 集群 API
- Cluster Allocation Explain API
- Cluster Health
- Cluster Reroute
- Cluster State
- Cluster Stats
- Cluster Update Settings
- Nodes hot_threads
- Nodes Info
- Nodes Stats
- Pending cluster tasks
- Task Management API
- 查询 DSL
- 查询和过滤上下文
- Match ALL 查询
- 全文搜索
- 匹配查询
- 短语匹配查询
- 短语前缀匹配查询
- 多字段查询
- 常用术语查询
- 查询语句查询
- 简单查询语句
- 复合查询家族
- Constant Score 查询
- Bool 查询
- Dis Max 查询
- Function Score 查询
- Boosting 查询
- Indices 查询
- Join 查询
- Has Child Query
- Has Parent Query
- Nested Query(嵌套查询)
- Parent Id Query
- 术语查询
- Exists Query(非空值查询)
- Fuzzy Query(模糊查询)
- Ids Query(ID 查询)
- Prefix Query(前缀查询)
- Range Query(范围查询)
- Regexp Query(正则表达式查询)
- Term Query(项查询)
- Terms Query(多项查询)
- Type Query(类型查询)
- Wildcard Query(通配符查询)
- 地理位置查询
- GeoShape Query(地理形状查询)
- Geo Bounding Box Query(地理边框查询)
- Geo Distance Query(地理距离查询)
- Geo Distance Range Query(地理距离范围查询)
- Geo Polygon Query(地理多边形查询)
- Span 查询
- Span Term 查询
- Span Multi Term 查询
- Span First 查询
- Span Near 查询
- Span Or 查询
- Span Not 查询
- Span Containing 查询
- Span Within 查询
- Span Field Masking 查询
- Specialized queries(专业查询)
- Mapping(映射)
- 字段类型
- Array
- Binary
- Range
- Boolean
- Date
- Geo-point datatype
- String
- Text
- Token数
- 渗滤型
- KeyWord
- Nested
- Object
- Numeric
- Meta-Fields(元字段)
- _all field
- _field_names field
- _id field
- _index field
- _meta field
- _parent field
- _routing field
- _source field
- _type field
- _uid field
- Mapping parameters(映射参数)
- analyzer(分析器)
- normalizer(归一化)
- boost(提升)
- Coerce(强制类型转换)
- copy_to(合并参数)
- doc_values(文档值)
- dynamic(动态设置)
- enabled(开启字段)
- fielddata(字段数据)
- format (日期格式)
- ignore_above(忽略超越限制的字段)
- ignore_malformed(忽略格式不对的数据)
- include_in_all(_all 查询包含字段)
- index_options(索引设置)
- index (索引)
- fields(字段)
- Norms (标准信息)
- null_value(空值)
- position_increment_gap(短语位置间隙)
- properties (属性)
- search_analyzer (搜索分析器)
- similarity (匹配方法)
- store(存储)
- Term_vectors(词根信息)
- Dynamic Mapping(动态映射)
- default mapping(mapping中的_default_)
- Dynamic field mapping(动态字段映射)
- Dynamic templates(动态模板)
- Override default template(覆盖默认模板)
- Mapping(映射)
- Analysis
- Tokenizers(分词器)
- Standard Tokenizer(标准分词器)
- Letter Tokenizer
- Lowercase Tokenizer (小写分词器)
- Whitespace Analyzer
- 停止分析器
- UAX URL Email Tokenizer
- Classic Tokenizer
- Thai Tokenizer(泰语分词器)
- NGram Tokenizer
- Keyword Analyzer
- Path Hierarchy Tokenizer(路径层次分词器)
- Pattern Tokenizer
- Token Filters(词元过滤器)
- Apostrophe Token Filter(撇号/单引号过滤器)
- ASCII Folding Token Filter(ASCII Folding 词元过滤器)
- CJK Bigram Token Filter(CJK Bigram词元过滤器)
- CJK Width Token Filter(CJK宽度过滤器)
- Classic Token Filter(经典过滤器)
- Common Grams Token Filter(近义词词元过滤器)
- Compound Word Token Filter(复合词过滤器)
- Decimal Digit Token Filter(十进制数字过滤器)
- Delimited Payload Token Filter(Delimited Payload词元分析器)
- Edge NGram Token Filter(Edge NGram 词元过滤器)
- Elision Token Filter(Elision词元过滤器)
- Fingerprint Token Filter(指纹过滤器)
- Flatten Graph Token Filter(Flatten Graph 词元过滤器)
- Hunspell Token Filter(Hunspell 词元过滤器)
- Keep Types Token Filter(保留指定类型过滤器)
- Keep Words Token Filter(保留字过滤器)
- Keyword Marker Token Filter(Keyword Marker 词元过滤器)
- Keyword Repeat Token Filter(Keyword Repeat 词元过滤器)
- KStem Token Filter(KStem 词元过滤器)
- Length Token Filter(长度词元过滤器)
- Limit Token Count Token Filter(限制词元数量过滤器)
- Lowercase Token Filter(Lowercase 词元过滤器)
- Minhash Token Filter(Minhash过滤器)
- NGram Token Filter(NGram词元过滤器)
- Normalization Token Filter(标准化词元过滤器)
- Pattern Capture Token Filter(模式匹配词元过滤器)
- Pattern Replace Token Filter(模式替换词元过滤器)
- Phonetic Token Filter(Phonetic 词元过滤器)
- Porter Stem Token Filter(Porter Stem 词元过滤器)
- Reverse Token Filteredit(反向词元过滤器)
- Shingle Token Filter(Shingle 词元过滤器)
- Snowball Token Filter(Snowball 词元过滤器)
- Standard Token Filters(标准词元过滤器)
- Stemmer Override Token Filter(Stemmer Override 词元过滤器)
- Stemmer Token Filter(Stemmer 词元过滤器)
- Stop Token Filter(Stop 词元过滤器)
- Synonym Graph Token Filter(Synonym Graph 词元过滤器)
- Synonym Token Filter(Synonym 词元过滤器)
- Trim Token Filter(Trim词元过滤器)
- Truncate Token Filter(截断词元过滤器)
- Unique Token Filter(唯一词元过滤器)
- Uppercase Token Filter(Uppercase词元过滤器)
- Word Delimiter Token Filter(Word Delimiter 词元过滤器)
- Character Filters(字符过滤器)
- md Strip Character Filter
- Mapping Character Filter
- Pattern Replace Character Filter
- Anatomy of an analyzer(分析器的分析)
- Testing analyzers(测试分析器)
- Analyzers(分析器)
- Configuring built-in analyzers(配置内置分析器)
- Standard Analyzer(标准分析器)
- Simple Analyzer(简单分析器)
- 空白分析器
- Stop Analyzer
- 指纹分析器
- 模式分析器
- 自定义分析器
- 语言分析器
- 模块
- Indices(索引)
- Circuit breakers(熔断器)
- Fielddata cache(列数据缓存)
- indexing buffer(索引写入缓冲)
- indices Recovery(索引恢复)
- NetWork Setting(网络配置)
- Node Query Cache(节点查询缓存)
- Shard request cache(分片请求缓存)
- 脚本
- Groovy 脚本语言
- Painless 脚本语言
- Painless 语法
- Painless 调试
- Lucene表达式语言
- 原生(Java)脚本
- 高级文本评分脚本
- 快照和还原
- 线程池
- 传输
- HTTP
- Tribe Node (部落节点)
- 跨集群搜索
- Cluster(集群)
- Disk-based Shard Allocation ( 基于磁盘的分片分配 )
- Shard Allocation Awareness ( 分片分配意识 )
- 群集级别分片分配
- Node
- 插件
- Index Modules(索引模块)
- Analysis(分析)
- 索引分片分配
- 分片分配过滤
- 节点丢失时的延迟分配
- 索引恢复的优先级
- 每个节点的总分片数
- Mapper(映射)
- Merge(合并)
- Similarity module(相似模块)
- Slow log(慢日志)
- Store
- 预加载数据到文件系统缓存
- Translog(事务日志)
- Ingest Node(预处理节点)
- Pipeline Definition(管道定义)
- Ingest APIs
- Put Pipeline API
- Get Pipeline API
- Delete Pipeline API
- Simulate Pipeline API(模拟管道 API)
- Accessing Data in Pipelines(访问管道中的数据)
- Handling Failures in Pipelines(处理管道中的故障)
- Processors(处理器)
- Append Processor(追加处理器)
- Convert Processor(转换处理器)
- Date Processor(日期处理器)
- Date Index Name Processor(日期索引名称处理器)
- Fail Processor(故障处理器)
- Foreach Processor(循环处理器)
- Grok Processor(Grok 处理器)
- Gsub Processor(Gsub 处理器)
- Join Processor(连接处理器)
- JSON Processor(JSON 处理器)
- KV Processor(KV 处理器)
- Lowercase Processor(小写处理器)
- Remove Processor(删除处理器)
- Rename Processor(重命名处理器)
- Script Processor(脚本处理器)
- Set Processor(设置处理器)
- Split Processor(拆分处理器)
- Sort Processor(排序处理器)
- Trim Processor(修剪处理器)
- Uppercase Processor(大写处理器)
- Dot Expander Processor(点扩展器处理器)
- How to(操作方式)
- 一些建议
- Recipes(诀窍)
- 索引速率调优
- 查询优化
- 磁盘使用调优
- Testing(测试)
- Java Testing Framework(测试框架)
- ( why randomized testing ) 为什么随机测试?
- Using the elasticsearch test classes ( 使用 elasticsearch 测试类 )
- unit tests(单元测试)
- integreation test(集成测试)
- Randomized testing(随机测试)
- Assertions()
- Glossary of terms (词汇表)
- Release Notes(版本说明)
- 5.3.0 版本说明
- 5.2.2 Release Notes
- 5.2.1 Release Notes
- 5.2.0 Release Notes
- 5.1.2 Release Notes
- 5.1.1 Release Notes
- 5.1.0 Release Notes
- 5.0.1 Release Notes
